Experimental verification of the explanation
of the functioning of the solar cell:
In 1904 Philipp Lenard observed that the surface of a metal exposed to light
loses electrons absorbed by light and becomes positively polarized.
The electroscope clearly showed this phenomenon. Nobody "saw" the
electrons!
But the electron "discovered" then was the only explanation.
It remains to be explained how light manages to absorb electrons.
Einstein detailed the phenomenon. Now solar panels are industrial products.
This explanation shows that light can be replaced by "illuminating"
the surface of the panel
with positive electrostatic polarities, which will absorb electrons.
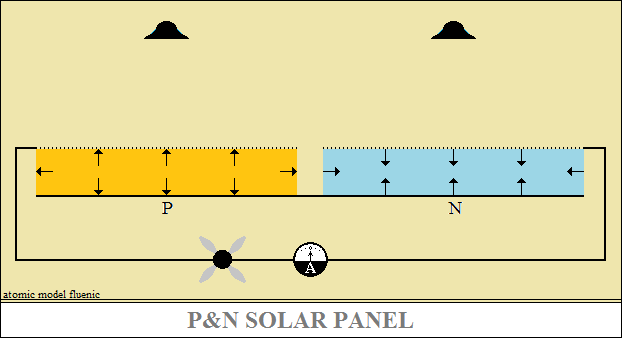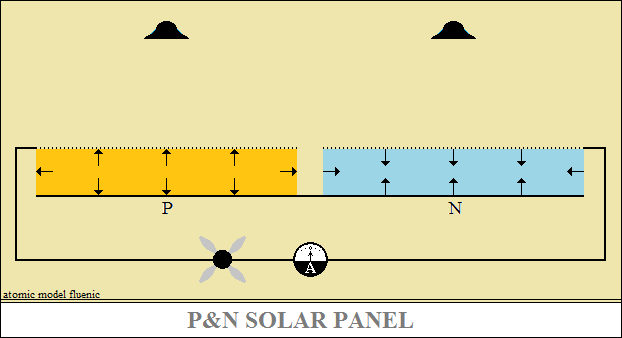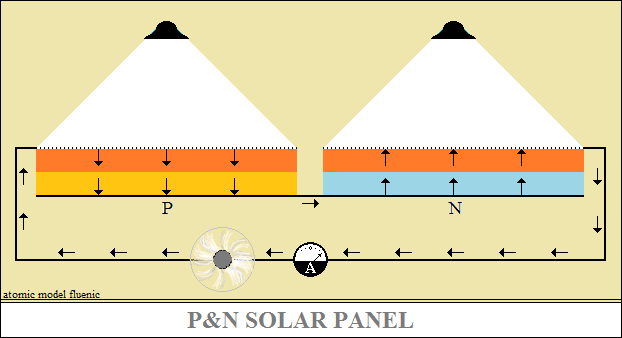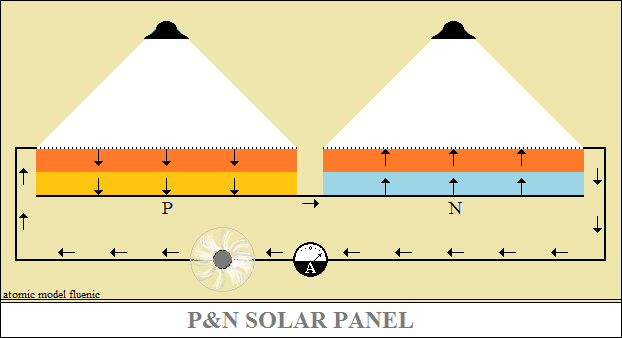
So, I put an aluminum foil on the surface of the panel,
polarized positive electrostatically (Van de Graaff) to "absorb"
electrons.
The negative result of the experiment demonstrates that the explanation
of the interpretation photovoltaic processes by the electronic theory of electricity
is false.
For the solar cell, the positive electrostatic polarization of the N layer
is equivalent
to the reverse polarization of a diode, the atoms negatively polarized
and the positively polarized atoms close each other and the N structure becomes
an insulator.
When the N layer is electrostatically negative polarized,
the state of the layer remains unchanged, equivalent to the lack of light.
Therefore, the interaction of light with the surface of a metal produces the
resonance
of the surface atoms, instantly heating them, the metal becoming a thermal
dipole.
In the case of N and P structures, they transforms each
into thermoelectric cells (Seebeck welds), which can be connected as Volta
cells.
This is the novelty revealed by such a simple experiment.
Attentively!
Positive or negative electrostatic (Van de Graaff) polarizations are not independent
electric charges.
There can be no independent electrical charges.
The repulsive forces of the substance are not due to polarization with the
same sign.
Polarizations are not gaps over gaps over gaps, or electrons over electrons
!!!
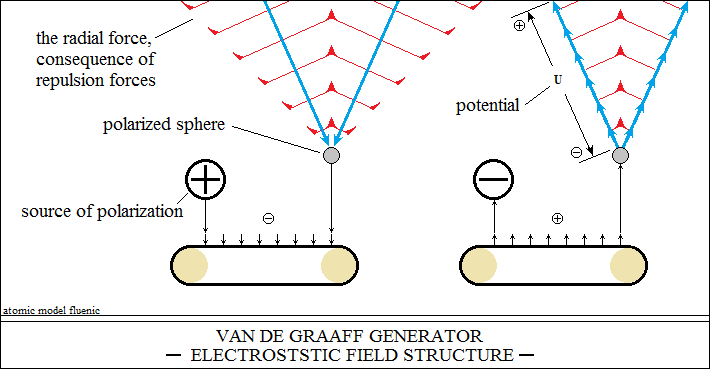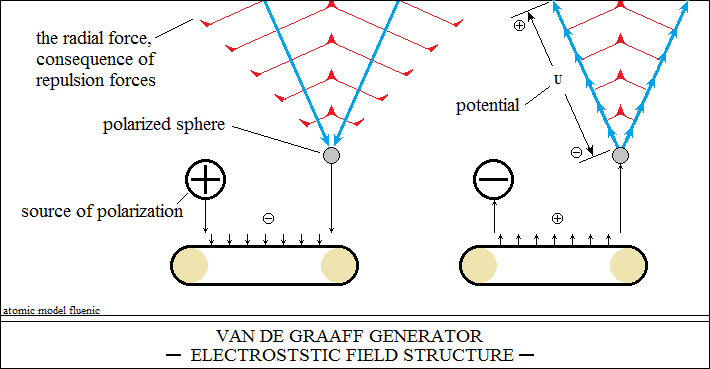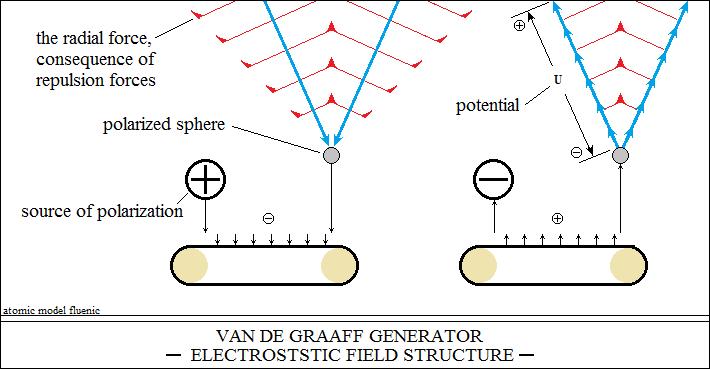
Van de Graaff electrostatic polarizations are open electrical circuits.
These circuits are composed of strings of vectors
related to the attraction between their opposite polarities.
Open electrical circuits are composed of vectors bonded in the same direction
and sense.
Open electrical circuits can be composed or decomposed into vectors, as can
permanent magnets.
The source polarizes the band with the reversed sense
and the band polarizes the sphere with the direct sense.
Vector polarities is reflected in the band as the ray of light into the mirror.
The positive or negative vector polarities applied in the structure of the
empty sphere,
orient in the same sense the polarities of the atoms from the surface of the
sphere.
Thus, the density of vector polarities increases and orients them in divergent
directions due to the spherical surface and the repulsive forces between them.
Radially oriented vectors, in turn, orient the vectors of space,
from close to close, the space being energy with vector properties.
In this way, with the increase of the circuit length, the radial electric
potential also increases.
This explains the millions of volts of the Van de Graaff electrostatic potential.
These strings, like the magnetic field lines, are purely vector circuits.
Open electrical circuits have divergently oriented vector polarities.
Divergent polarities with the base into source vectorially polarize the conveyor
belt.
Divergent polarities with the base into band, vectorially polarize the sphere.
Divergent polarities with the base into surface of the sphere polarize space
vectorially.
The direction of the polarization process of the sphere is mediated
by the conveyor belt only in the direction of movement, the belt being an
insulator.
Polarization processes are produced by the attractive forces
between the oppose polarities of the vectors.
Open vector circuits have a fixed base in the atoms of the sphere
and the repulsive forces print divergent directions, so they cannot be parallel.
The totality of open vector circuits constitutes the radial electric potential
of the sphere.
The structure of the radial electric potential is naturally associated with
spherical geometries (curves).
The repulsive forces between the open circuits are perpendicular to the direction
of the circuit.
The circuits being perpendicular to a spherical surface, the repulsive forces
close a circle.
From the vectorial compose of these forces,
results the radial acceleration of the circuit and of the substance.
The "electrostatic" field produced by any polarized body
is a sample of the structure of vector space.
The bodies of the universe are surrounded by force fields,
by vector structures, which constitute the notion of space.