
|
Civilization is the knowledge of nature.
|
Civilization is the knowledge of nature.
|
|
|
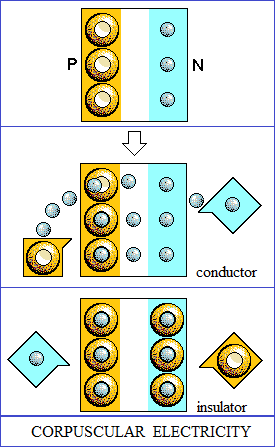
CORPUSCULAR INTERPRETATION OF EXISTENCE
Existence consists of the atoms that make up matter. |
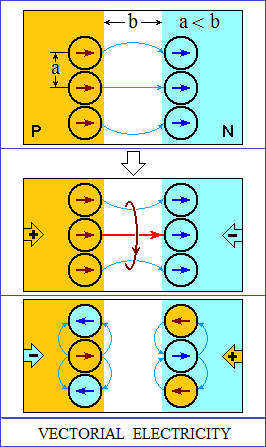
VECTOR INTERPRETATION OF EXISTENCE
Existence is energy with vector properties. |
|
|
GENESIS.
Existence began with the Big Bang, which hierarchically formed the atomic structures of matter. So the expansion of the universe show like the big bang continues. |
GENESIS
The interactions of vector properties give stable shapes (and ephemeral), in which the kinetic and potential state of energy oscillates (under the action of centripetal forces) - the double torr oscillator (the hydrogen atom). The centripetal force compresses the hydrogen into stars, where it multiplies. Thus, from the stars, star and galactic systems develop - (expansion). |
|
|
Atom.
Atoms make up material structures, have a positive electrical nucleus, around which orbit electrons, independent particles, mobile in structure and carrying negative electrical charges. |
Atom
In the double torr oscillator there are two identical vector circuits, orthogonally coupled, each passing through the other, changing reciprocally and alternately the kinetic and potential state of energy. The oscillations of the energy states become properties a autonomous corpuscle, which can produce induction in the vector space. |
|
|
THE FENOMENA OF THE NATURE.
The space. Space is still a controversial topic, I'm just considerations of some thinkers: Democritus; Epicurus; Aristotle; Engels; Kant; Hegel; Einstein ... |
THE FENOMENA OF THE NATURE.
Space Space is energy with vector properties. It is composed of all the vector interactions of bodies. It is the medium of propagation of vector oscillations, including through the structures of bodies, themselves being space. So space has a heterogeneous structure and is infinite. |
|
|
Time.
It does not have a consensus on the definition, but there is talk of a possible "time travel". |
Time
Time is the measure of transformations in structures matter, through incessant vector interactions. |
|
|
The force..
Four fundamental forces are established: gravity; electromagnetic force; weak nuclear force; and strong nuclear force. |
Force
The property of attraction and repulsion vectors is fundamental force, which circularly bond vectors of the space and composes two orthogonally coupled circuits. Each circuit is a spectrum of centripetal forces, with maximum limit at the center. It is a component of the structures of matter, from the microscopic to the galactic level. |
|
|
Gravity.
It is the force of attraction between bodies, the universal attraction, different from electric and magnetic forces. |
Gravity.
Gravity is magnetic force. The property of vectors, directivity, produces centripetal force in closed circuits and centrifugal force in open curves. |
|
|
Energy.
Energy is the scalar measure of the motion of matter. |
Energy.
Energy consists in the interactions of vector properties: force, directivity, orthogonality and meaning. |
|
|
Electricity.
Electricity is a set of associated physical phenomena with the presence and movement of electrical charges. |
Electricity.
The electricity are closed vector circuits. In conductors, vector circuits are the bonding circuits of atoms in the structure, broken and reoriented. |
|
|
Magnetism.
The stellar magnetic field is a generated magnetic field by the movement of a conductive plasma inside the star. |
Magnetism.
Magnetism is the force of the universe, the seen as "gravity." The core of the stars is a closed vectorial circuit (electroid), with zero Kelvin temperature. Fantastic circuits produce fantastic magnetic fields (space). |
|
|
Electrical current.
Represents the directed movement of electrical charges. |
Electromagnetic polarization (current).
In the conductor, electricity is not a current of scalar particles, it is not a "flow" of electrical charges. Electricity are the bonding vectorial circuits of atoms in the structure, broken and reoriented in a closed circuit. |
|
|
The effects of electromagnetic current.
Thermal effect or Joule effect, produced by friction of electrons in movement through the structure. The appearance of a magnetic field around the conductor. |
The effects of electromagnetic polarization.
The linking circuits oppose of ruptures - resistance. Breaking the bondings produces electric arc - thermal effect. |