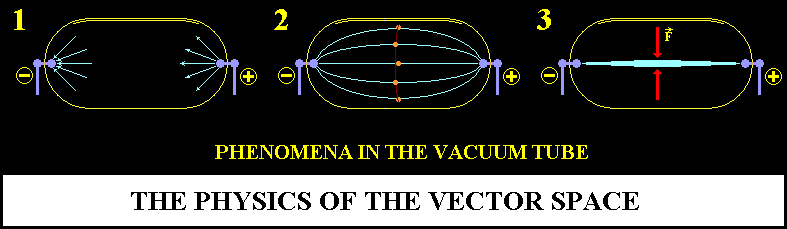
The
electric current into rarefied gas
The vacuum tube - valuable experimental device.
Connected to a source of current, the tube contacts are open, like reinforcements
of a condenser.
Therefore, electric polarities appear on contacts with the intensity of
the potential of the feeding source.
If the potential increases, the electric polarities unify in parallel
currents and close the circuit.
Around closed polarities, there appears orthogonal (magnetic) current
and triggers the centripetal interaction (condensers explode).
The electric and magnetic field, being vectorial space, electromagnetic
interactions are vectorial intraction.
If there are rarefied gases in the tub, their polarities are stringed
up on vectorial currents,
like breads and are accelerated in the axis of the interaction.
In the axis of interaction, the atoms crossed by the currents, release
visible oscillations.
The axis, being effect of centripetal vectorial interaction (electromagnetic),
interact obviously, with the corresponding external actions, with or without
gas into tube.