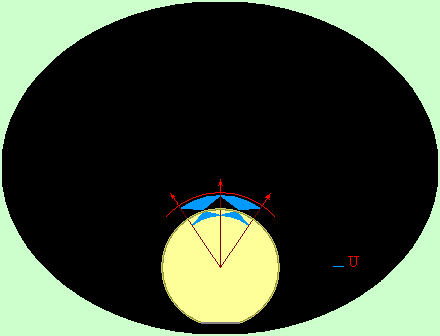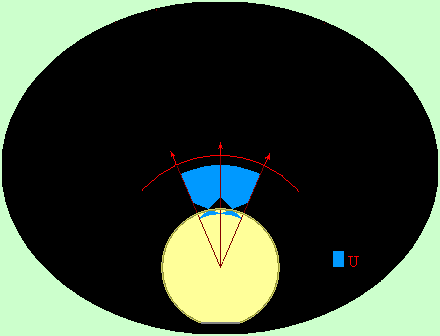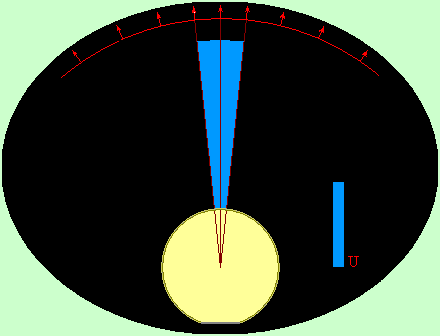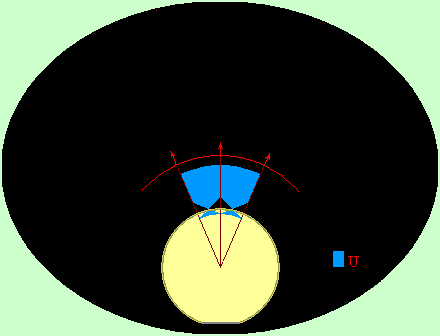
Effect
of sphere (drop, cylinder, sharp peak)
-
Different
- The
nucleon is an electromagnet, the photon as well. Plus polarity cannot be
detached, broken from minus polarity, in the same way that the north polarity
cannot be detached from the south polarity of a magnet. Fluenic hydrogen
is polar (it forms molecules). The planetary atomic model has independent
"electric charges". The hydrogen atom has positive charges in
the nucleus and negative charges in the electron. The two types of charges
having "amounts of electricity" equal with one unit, cancel each
other out. Planetary hydrogen is neutral. The electric properties
of the two particles "vanish"! In fact, they "take the role
of gravity". The electron can leave the atom, leaving there its positive
pair. It becomes free to participate in other interactions. If the electrons
are "brought" on the terminal of a condenser, we find on the other
armature positive charges! As if the two polarities have been inseparable.
Separation is the result of interpretation of electrification by friction.
Fluen males a simple interpretation: Nucleons, like atoms, bond with electric
polarities. The friction between two isolators breaks the bonds of the atoms,
new bonds are created, even between the two bodies. As a result of the friction,
part of the atoms remain with open polarities - "electrified".
In conductors they would have been neutralized. The tape of the Van Der
Graaf Generator transports "electrifications" - information. The
brush reads the tape, loads the memory of the sphere, elevating the density
of polarization. Therefore, tension = density of the orientation of fluen.
The cupola has a spherical form (essential!) Here the properties of the
electric dipole (electricity) manifest. In polarities, the orientation of
fluen is divergent, the lines reject each other and close at the opposed
polarity. The inside of the sphere gathers in a convergent way towards
its center all the field lines. Their rejection force sinks the polarities
in the metal and favours neutralization. The outside of the sphere
directs in a divergent way the polarities and the field lines. Their rejection
force draws the polarized atoms towards the exterior, "fixes"
their position on the surface of the cupola, canceling the possibility of
neutralization. However the increase of polarization of other atoms (tension)
continues. Tension makes a file of the polarities of atoms of the nearby
gases, their file lengthening itself proportionally with the tension. When
the end of the file touches a conductor having electric capacity, the file
becomes a conductor between two capacities. The current passes through the
gas atoms, the electric polarities absorb the energy, releasing photons.
This is how the spectacular optical and acoustic phenomena appear.