requires detailed explanations
to be understood.
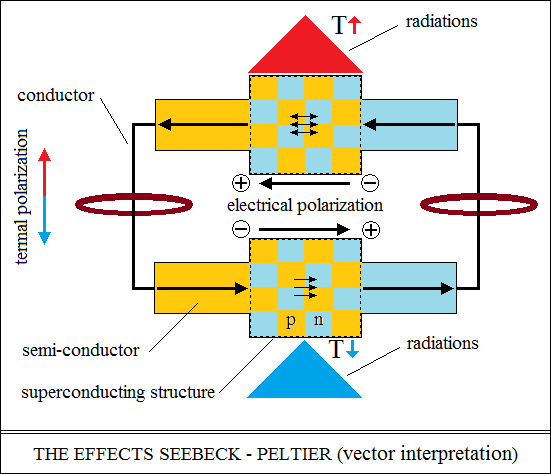
The semiconductor junction P and N by welding
has no net boundary between semiconductors, it is not a diode.
Under the welding process, the pn semiconductor atoms establish current
connections, resulting in an electrically polarized structure in the direction
and sense.
This stable polarized structure is a current source, a voltaic cell without
chemical transformation.
The source is highlighted by the Seebeck effect, which, by heating a junction,
closes the electrical circuit through the other junction.
The heating of the structure tear the currents of atomic bonds and is
pierced by the electromagnetic current generated by the polarities of
the other structure,
The electromagnetic force tends to orient the open polarities at level
the intensity of the structure.
The polarities of atom are of the bond current, open-loop current.
Electromagnetic oriented polarities become intensity I,
and if they oppose the orientation, they become resistance R.
Open polarities also interact with electrostatic forces.
On the one hand the attraction of the opposite polarity (interrupted bond).
On the other hand, the rejection of polarities of the same sign (the polarities
already oriented).
The polarities oscillations between intensity and resistance are emitted
by the atom (thermal effect).
Directly powered in closed circuit, the source structure does not emit
oscillations.
Atoms of the structure do not oscillate, the electrical parameters do
not vary.
The intensity I is the polarization density in the section of the structure.
Resistance R is zero, polarization orientation being the connection currents
in the structure,
not electromagnetic. Potential U = RI = 0.
So the absorption of oscillations in the structure does not produce variations
in voltage and strength, because these electrical parameters do not exist
in the structure.
The structure produces the transition of the incident oscillations in
the current (photoelectric phenomenon!), Which reaches directly into the
connected circuit and there produces variations of resistance and emit
thermal oscillations (electrofotonic phenomenon!).
Details
The thermoelectric generator produces two interconditioned polarizations:
Thermal polarization produces the sense of the electric current and vice
versa.
Thermal polarization is the differentiation between absorbtion / emission
processes.
This differentiation is the essence of the thermoelectric phenomenon and
the prelude of future devices for the transformation of current into radiation
and of the into current radiation.
In atoms, the absorbed oscillations have transient states (in current),
which may be limited or permanent (photosynthesis link currents).
This interpretation justifies the structure of the welded pn junction
of the oriented electric polarities,
this being the currents of the atomic bonds in the structure.
Oscillations are information, and the structure acts "as a single
atom"
but with a multiple transition capability in time and intensity.
The oscillations transformed in current (rectified) goes into the circuit
as a current source.
The structure is an empirical achievement and will be studied and used
in the future.