Implications of the electroide
in the knowledge of electrical phenomena.
The electroide cannot be a "current of electrical charges."
Electric current, electric charges do not exist,
are primitive interpretations of the electrical phenomenon.
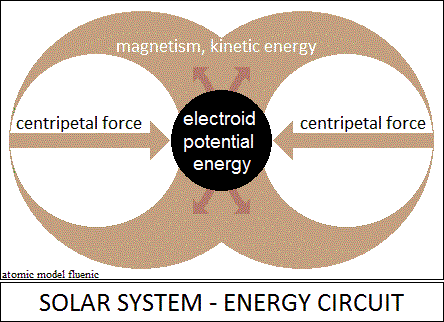
The electroide is the potential state of energy with vector properties,
existentially related to the kinetic state.
The kinetic state of energy are the vector properties in action, which not
seen, not heard.
Of the properties, only the force (centripetal) was perceived, which Newton
called gravitation.
The potential energy of the solar system, the electroide, continuously produces
kinetic energy, the magnetism of the system and simultaneously, the magnetism
of the system produces the electroide.
The potential state of energy, the electroide, does not oscillate alternatively
with the kinetic state, as in the other vector oscillations.
Potential energy and kinetic energy, electricity and magnetism,
"flow" continuously with the speed of light one in the shape of
the other.
The phenomenon can be compared to the water circuit in nature:
Let's imagine the potential energy of an accumulation lake, which flows rapidly
in the hydropower plant, evaporates and the vapors condense returning to the
lake.
Part of the kinetic energy, converted into electricity, was used from this
circuit.
The comparison is different in the case of an electric car battery:
The battery is a potential source of energy.
The energy of the source consists in the orientation of the vector polarities
in the same sense.
The consumption of potential energy is its conversion into the kinetic energy
used,
when the orientation of the polarities come back bonds in source structure
again.
The depleted potential energy source is recharged and the cycle is repeated.
The thought flees to the above phenomenon, the unloading and loading to be
in a closed circuit.
The idea is that the magnetism of the closed circuit is to be used to reorient
the polarities
of the source (the phenomenon of electricity propagation in closed circuits).
This mode does not need large (backup) sources.
Something new, always starts with experimental variants:
At first, to by experiment on batteries with chemical structures.
Gradually, the chemical structure will be abandoned, as in the case of the
diode,
the glass flask and the variable air condenser were abandoned.
The phenomena from graphene and from the Seebeck experiment can be considered
for the realization of a solid source with electric potential,
in which the charge itself (kinetic energy) to regenerate the potential energy.
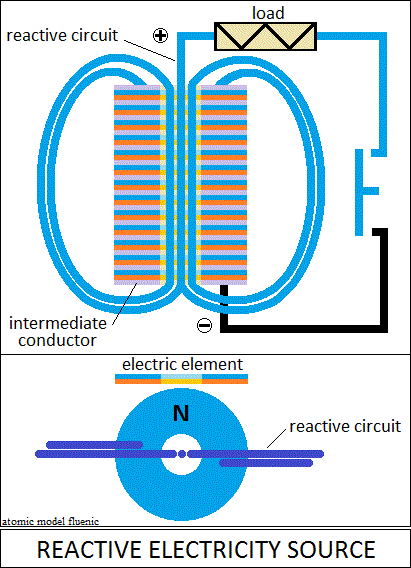
The drawings show schematically the connections of the elements in the circuit:
Source, consumer and reactive circuit.
When the circuit closes, the source loses the oriented polarities
that have become kinetic energy, and the reactive circuit reorients them.
The role of the reactive circuit is to produce centripetal EM force
on the source, limiting the discharge in proportion to the load.
The Seebeck experiment.
In the Seebeck experiment, the two welded contacts
are electrically polarized by the pn structures.
Polarities with opposite sense, one stops the propagation of the other.
By heating a weld, the polarities of the atoms gain freedom of orientation
and the polarities cold, propagate and closing the circuit.
Heated welding can be replaced by an intermediate conductor (graphene?)
and a process that closes the electrical circuit without other contact polarizations.
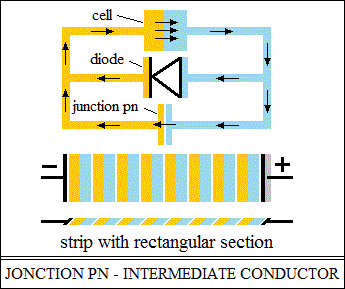
The welding of PN semiconductors forms an area with stable atomic bonds (EM),
in which the electrical polarities are oriented predominantly with the PN
direction.
The electrical polarization PN is similar to the magnetic polarization NS.
Electrization propagates in a closed circuit, as magnetization.
Making an electrical element.
PN semiconductors in the form of very thin blades, glued by electric welding
(DC),
can be stamped in the form of a flat washer.
Very thin, so as not to form other polarizations with the intermediate conductor.
Electrically welded (DC) to increase the density of oriented polarities.
Such flat washers, electrically polarized, are the elements that makes up
a battery.
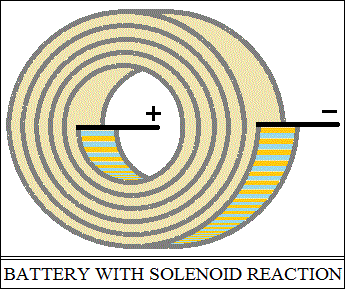
Solenoid-shaped battery variant.
This variant closes the energy circuit even more.
The intermediate conductor being a diode, respectively a pn junction,
the battery becomes a conductor with cylindrical or rectangular section.
The reactive circuit is a form of solenoid.