Repeat,
repeat, for children to understand
The operation of an electromagnetic stationary oscillator:
The explanations are reasonable and logical, only if we admit the vector
nature of space.
In the vector space, we consider a close vector current, a ring, an "electric"
torus
The electric torus being vector space, induces around it a "magnetic"
torus
The two toruses orthogonally connected, like two chain links,
compose a centripetal electromagnetic interaction.
This is a stationary electromagnetic oscillator, with conserved place
and energy - a nucleon.
Who a traveling electromagnetic oscillator is issued and propagated:
When a nucleon receives energy from the outside, its oscillation releases
the energy pulse, in the shape of an "electric" torus.
Releases a foton!
The electric torus induces all energy making orthogonally a magnetic torus
and "disappears"
The magnetic torus continues the oscillation of the wave, inducing a new
precise electric torus in the opposite part of that disappeared therefore,
the place of the electric torus was "moved" (induced) from the
back to the front, stepping in space (propagation). This is the traveling
electromagnetic oscillator! - foton
Each induced torus, once translated on the propagation direction, induces
transversally displaced polarity by 90 degrees, the oscillator induces
therefore a rotation as well.The rotation speed is equal to half of the
frequency (f / 2)We keep in mind that the foton is an electromagnetic
wave, a orthogonal vector oscillator (a sphere), which is propagated in
the vector space, with translation, rotation, energy, frequency and wavelength
constants.
We tell children in elementary school that the foton has two feet: electric
and magnetic.
Electromagnetic wave is propagated as oscillation volume and has the geometry
of elongated sphere on the direction of the propagation. The volume of
a foton s determined by the wave length.
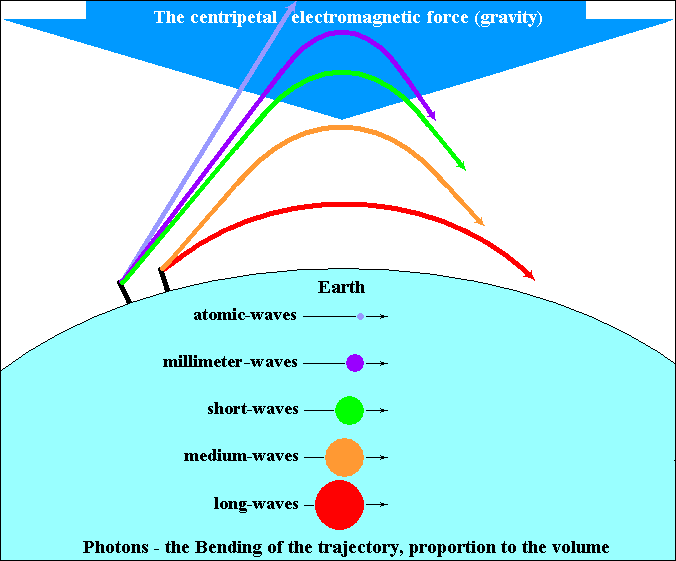
Space and gravity (centripetal electromagnetic force), shows its electromagnetic
nature, curving foton trajectory, proportionally to their volume (erroneously
assigned interaction, ionosphere reflection)The space composes centripetal
electromagnetic interaction and with it, composes, connects and makes
material structures.