Electron microscope
The electron microscope started from the idea of increasing the performance
of the optical microscope, by using an electron beam.
Vector microscope
The high voltage used electrostatically polarizes the cathode with negative
polarities
and the anode with positive polarities.
The material particles are removed from the vacuum tube, but not the vector
space.
The cathode and the anode spaced apart, polarizates
the space vectors forming a capacitance, the circuit remaining open.
The bonds of the atoms in the structure of the heated cathode acquire freedom
of orientation,
as in the heated structure of the Seebeck effect.
The polarization density of the cathode increases
and electrostatically closes the circuit with the positive polarities of the
anoduct.
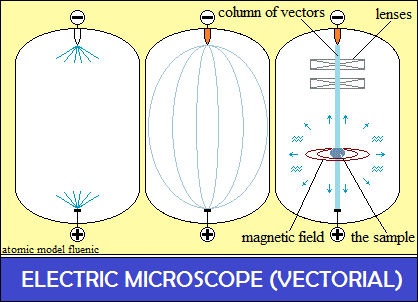
The vector space in the tube was electrostatically polarized,
connecting the cathode and the anode with a vector column.
The vector column did not come from either the cathode or the anode,
The tube space vectors simply connected the cathode to the anode.
The parallel oriented polarities are rejected and the column takes the form
of a "barrel"
Source of informative images
The sample is placed in the column of electrostatic polarities, previously
aligned conveniently.
In the sample column it is integrated like a conductor, with the electrical
dimensions: U, I and R.
The interaction of the column with the sample consists in breaking the electrical
bonds
of the atoms in the structure and their orientation in the column.
The orientation of the electrical polarities of the atoms in the column
also orients their magnetic circuits, producing centripetal force.
The atoms of the sample and the breaking of the connection circuits (with
arc),
emit an omnidirectional spectrum of electromagnetic oscillations - the source
of informative images.
The centripetal force increases with the electric potential, respectively
with the density of the polarization of the sample, until the volatilization
of the sample.
But, a slight variation of the electric potential, prodce " resonance"
in the sample structure,
like magnetic resonance in MRI technology.
The information is the images of the emitted frequencies, captured from different
angles.
Images can be captured in color by the cameras that discern the frequencies.
Comparison
In the electron microscope the images of the sample are collected
by a beam of electrons through mechanical interactions.
In the vector microcup, the images of the sample are their own radiation.