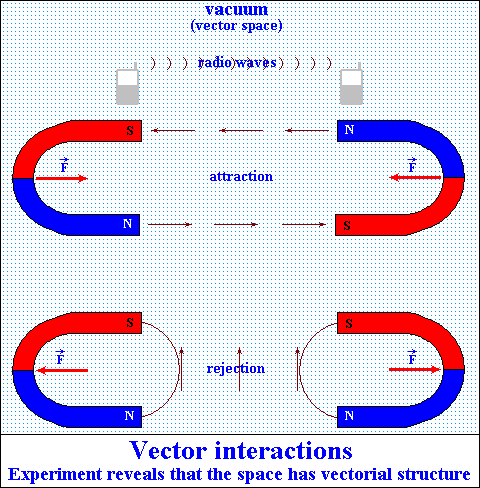
The
interactions from distance, reveals that the space
has vectorial structure.
Consequently, a new atom model and new interpretations of natural phenomena.
What is matter?
1) The corpuscular interpretation
A material body cannot be divided to infinity.
When it cannot be divided anymore, it becomes "matter that cannot
be divided" - atom
Explained, matter is composed of…matter (that cannot be divided)
After more than two thousand years, John Dalton ascertains the existence
of the atom, by experiment.
The findings of John Dalton produces the frenzy of the idea behind the
atom.
Every phenomenon must have its own atom:
Electricity - the electron
Magnetism - the magneton
Light - the photon
Gravitation - the graviton
The energy does not divide to infinity either!
There is a very small quantity of energy - the quantum!!!
What is matter?
2) The vectorial interpretation
The interaction from distance:
Two magnets interact from distance, even in vacuum.
Logically, if the interaction exists, there must be an intermediate for
this interaction,
something that would allow the communication, action and properties of
the magnets.
What are the properties of the magnets? Direction, sense and force.
These are the properties of a vector.
Thus, the interaction between magnets leads to the conclusion that the
space has a vectorial structure,
which we named field: electromagnetic field, gravitational field, fluen,
ether, etc.
How do we interpret the vectorial space?
The image of a vector, the vector of existence, is the symbol of
the properties of the space.
These properties are demonstrated in an experiment - direction, sense,
force and orthogonality.
The vector of existence, is the line that separates the known from the
unknown or the existence from the insistence.
The movement, the oscillation of the vectors, shows the existence of the
time
and the properties of substance - matter (under the form of vectorial
oscillators, hydrogen).
The property of force, of energy, is similar to the property of orthogonality
as they produce
centripetal vectorial interactions, from nuclear level interactions (hydrogen)
to the galactic level interactions.
Temperature - the level of radiation emitted by the oscillations
of a vector structure
Orthogonality - the organization property of the vector space,
in currents, mutually orthogonal.
Combining this interactions, the space becomes organized.
Example:
The centripetal vectorial interaction in the arc (metal welding), contains
a multitude of other centripetal interactions,
at the crystal bonds level (with higher frequencies), having as consequence,
the effects of the arc.