Brownian motion.
The vector space, the forces of attraction between the polarities of the
vectors, formed microscopically, orthogonally closed vector circuits,
hydrogen atoms. In orthogonally closed circuits, the additivity of the
vectorial forces of attraction tends to zero, they shorten the length
of the
circuits and produce centripetal forces, pressure. Vector circuits are
not
singular "wires", they are vector space, force field, as Faraday
said.
The centripetal forces of these fields compress each other, until a balance,
forming the core of the vector structure. The nucleus, of orthogonally
closed
centripetal forces, enters oscillations only when forces in the vector
space
break the balance of forces. Therefore, orthogonally closed vector circuits,
hydrogen atoms are the properties of the vector space, structures with
objective forms, "matter", the starting argument of the materialist
conception.
The vector space being the reference system, with its properties to form
atomic
structures, it is also the cause of the movement of atoms. In the universe,
the
nuclei of the vectorial, microscopic and macroscopic structures are continuously
moved by the vector space. The oscillations of the orthogonally closed
vector
structures of the hydrogen atom generate a spectrum of frequencies, with
extension, depending on the forces of space. The kinetic energy of the
frequency spectrum, the reaction of the propagation force, produces
vibrations of the nucleus, movements in relation to the referential vector
space.
The hydrogen of water molecules, the propagation of spectra in vector
space,
produce interactions between molecules, the Brownian movements seen
under a microscope. Experimental particles float on the movements of water
molecules, like Venetian gondolas on the waves. The centripetal forces
of the
orthogonally closed vector circuits in the nucleus of the hydrogen atom
prove
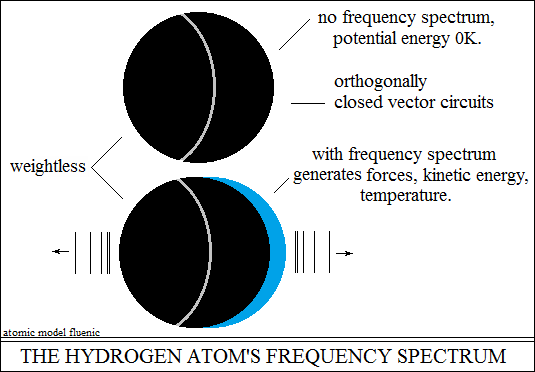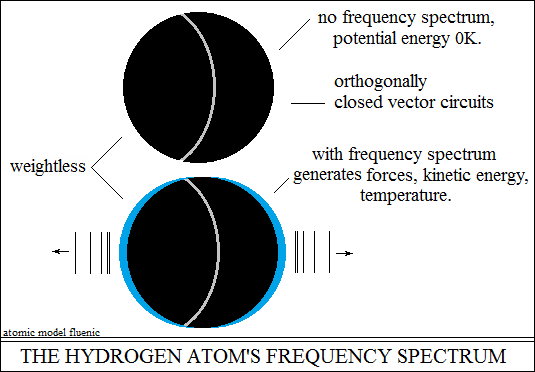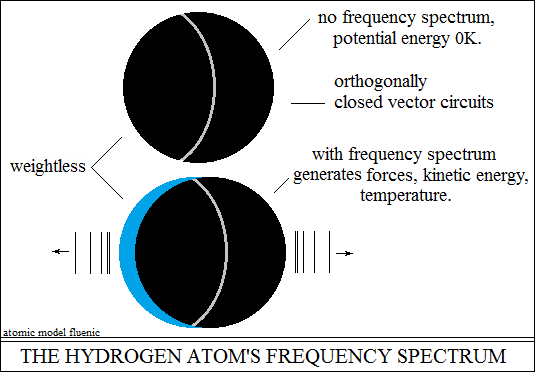
that they are a kind of static capacity in equilibrium. The hydrogen nucleus
is potential energy, it does not produce oscillations, it does not produce
temperature (zero K). Upon the action of an external stimulus, the two
centripetal forces go out of balance and generate a spectrum of characteristic
oscillations, kinetic energy, temperature. When the external stimulus
ceases,
centripetal forces return to equilibrium, they do not oscillate by themselves,
they maintain static equilibrium. In the universe,
dark matter are clouds of static, invisible hydrogen nuclei.
Conclusion.
Brownian motion, differential rotation motion and centripetal force
misinterpreted as "universal attraction" are effects of the
interactions
of the referential vector space, with its objective structures.
The frequency spectrum of the hydrogen atom, the oscillations
of the closed orthogonal vector circuits, produce the following effects:
- propagate forces, oscillations in the vector space (radiation, energy,
temperature).
- the spectrum, solidary with the vector space, produces vibrations of
the nucleus. -
- the space with the forces of the propagated atom spectra, moves the
atoms. -------
The effect of the Brownian movements, called temperature, presents the
poses:
- the temperature of living organisms, regulated metabolically. ---------------
- the temperature of the stars called plasma, of the planets called lava.
-----
- temperature of friction and fire, called chemical reactions. -----------------
The atomic frequency spectra, the centripetal forces of the orthogonally
closed
vector circuits, mutually antagonistic, propagate in the vector space,
forces
of attraction and repulsion, whose interactions change the distances between
objects. Apparently, objects move in space, get closer, or move away.
In reality, the vector space, the oscillations, which we perceive as light,
color,
temperature, distances, bring objects closer or further away. The properties
of the vector space are highlighted by the images of the Hubble telescope.
In vector space, only animal organisms can move by themselves.
Fusion fission.
The centripetal forces of the orthogonally closed stellar vector circuits
compress the plasma spherically and increase the hydrogen density, and
the
(electromagnetic) pressure increases exponentially towards the center.
The hydrogen molecule is formed at a certain density of kinetic energy,
of
radiation. At that density, the vector space between two atoms closes
common vector circuits through the polarities of the two atoms.
The centripetal forces of the common circuits shorten the distance
between the cores. The orthogonal circuits of the two nuclei reject the
approach.
The increase in attractive forces as they get closer overcomes the repulsion
of the nuclei and forms a new vector structure - the hydrogen molecule.
The atoms of the elements are bonds composed successively, with the
same centripetal forces, one atom, two atoms or four atoms simultaneously
(helium) - fusion. The nuclei that have the four polarities linked are
called
neutrons. The reverse reaction of the fusion, the fission, the internal
forces
of repulsion, spontaneously emits the precariously added
peripheral nuclei and gamma radiation - radioactivity.
The high density of radioactive elements produce chain reactions.
Reactions, collisions and ruptures are characteristics of the materialistic
conception. In the vector interpretation there are interactions of the
vector
properties. Nuclei are linked by closed vector circuits with their attractive
forces. Link circuits are potential energy, without oscillations (electricity).
The entry into oscillations of the connection circuits, transforms potential
energy into kinetic energy, oscillations, temperature and saturates the
surrounding environment. The interactions of the environment break other
nuclear bonds and exponentially amplify the radiation, emitted into
the vector space, with already observed effects - nuclear fission.