The
nervous system is an electromagnetic phenomenon
The morphological description of the nervous system
is just the beginning of knowing its functioning.
The vectorial Interpretation.
The nervous system operates with the properties of vectorial (electromagnetic)
oscillations.
Overview
The substances, the organisms, are composed of vector electromagnetic
oscillators.
Electromagnetic waves are incompatible with electrical charges.
The nervous system is the most complex
use of vector interactions - oscillations, frequency, and energy.
The nervous system coordinates the body's relationship with the external
and internal environment,
through sensory and reason organs, using EM oscillations.
Sensory stimuli are the frequencies of electromagnetic oscillations.
The nervous system receives oscillations from the sense organs
and transmits them to the internal structures through the network of nerves
(waveguides)
in the form of pulses, oscillations trains, radar-like.
The oscillations received from the sense organs
also have wavelengths incompatible with the nervous system.
The body has "developed" technical procedures for processing
them.
The demonstrating example is the functioning of the hearing organ:
The hearing organ.
The "mechanical" oscillations in the acoustic field are concentrated
in the cochlear fluid on Corti's organ.
Corti's organ overlap the acoustic frequencies on oscillators with neural
frequencies.
It is similar to the radio overlapping of the information on the carrier
frequency.
The frequency of neurons modulated with acoustic frequency reaches the
SNC
and accesses the information from the memory, with which it resonates.
Processed resonance is sent to the speech apparatus, which reverses the
function of Corti's organ.
The brain
The brain is an electromagnetic oscillators structure,
specialized in processing information in the form of oscillations with
certain frequencies.
Frequencies from the external environment and those necessary for the
body's functioning
are stored on the oscillators structure.
Accessing is rational (volitive) and relational in response to stimuli.
The phenomenon of selecting information from memory is the resonance.
Resonance also produces the force of the movement organs.
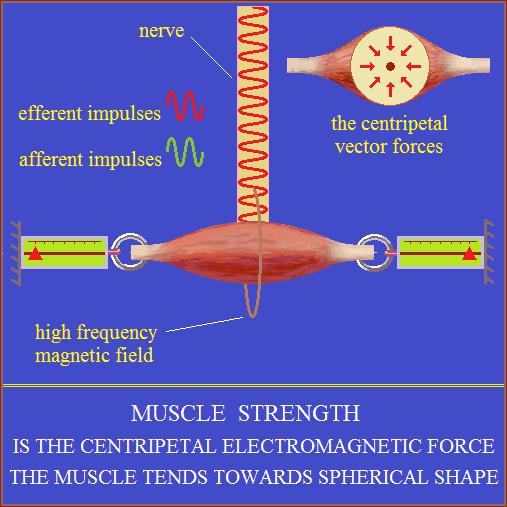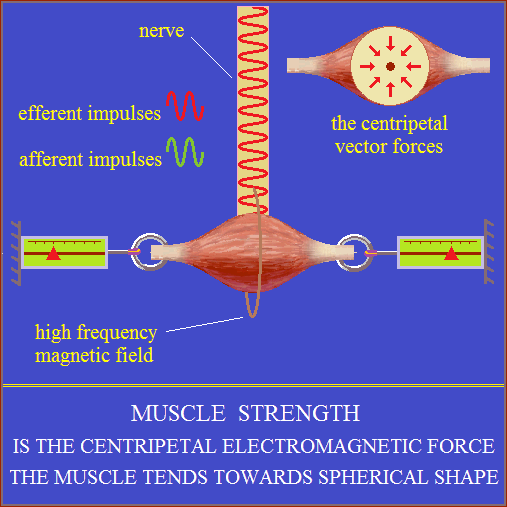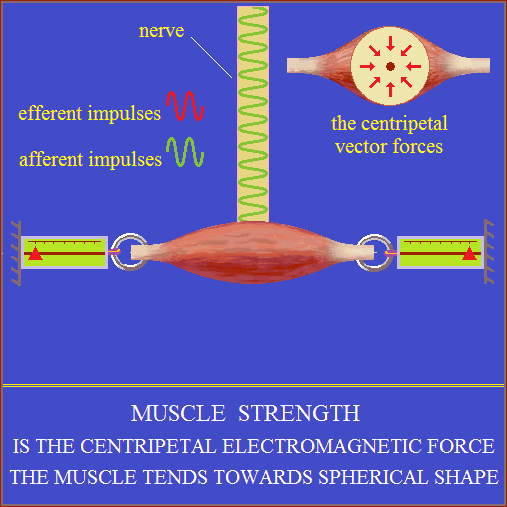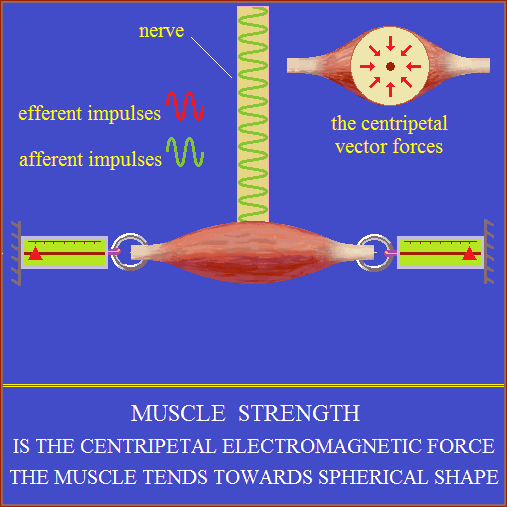
Muscle force
Let's recall the EM forces of the electric arc.
The electric current threads with the same direction and sense,
produce the centripetal electromagnetic force and axial forces of attraction
(electrolysis).
If we change the polarities of the current, the meaning of the magnetic
field changes, the centripetal force remains centripetal, the axial forces
remain axial.
So in alternating current the axial forces in the electric arc remain
axial.
Biological electric arc.
The muscle cell and its components are EM oscillators.
A string of muscle cells is like an open electric conductor.
More of such strings united at the ends form a muscle.
Nerve impulse (electromagnetic oscillations) when it reached at muscle,
brings the oscillations of muscle cells into resonating (PLL?).
Resonance means the synchronization, amplification
and integration of electromagnetic oscillations of muscle cells.
Integration of electromagnetic oscillations produces forces similar
to those the high-frequency alternating current arc!
The muscle tends towards spherical shape.
Muscle fibers adopt the optimal form of the function.
Effects of muscle tissue
- Muscle tissue is a source of energy,
- Show loading and unloading - bodybuilding and atrophy.
- Develops mechanical force relative to the intensity of the nervous impulse.
- Emit thermal radiation that maintains the thermal balance
of the body - the tremble, hibernation.
- Emit optical radiation used by organisms of the animals from the oceans
depth
Anomalies of muscle tissue.
- The resonance by other causes - cramps.
- The resonance at the electrocution - the Galvani effect.