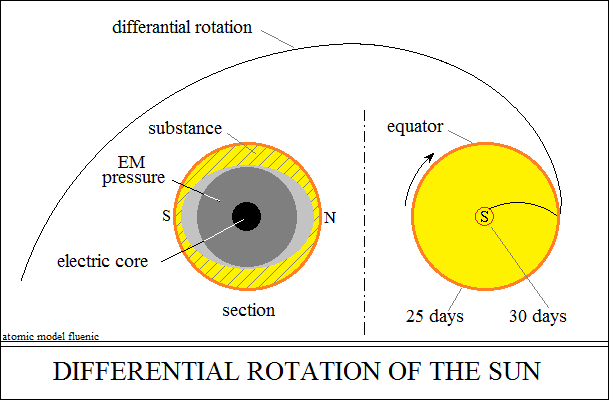
Differential rotation
of the sun.
Explanation of the differential rotation of the solar spherical gas.
The sun rotates like the earth, except that the rotation speed of the
gas
decreases progressively and symmetrically, from the equator to the polar
latitudes. The universe is vector energy, whose interactions, (laws of
physics)
mostly known, take the form of "matter", of objects. The characteristics
of
the sun object are its spherical shape, optical radiation, rotational
motion and
huge magnetic field. Of course, they are effects of internal causes, hidden
in
the gas sphere. The internal structure of the sun consists of two orthogonally
closed vector circuits, "electric and magnetic". So, the huge
magnetic field,
kinetic energy is generated by an electric circuit, potential energy equivalent
to
the energy of the magnetic field. The circuits being closed,
generate centripetal electromagnetic force.
The effects of the centripetal electromagnetic force.
This force is called voltage, electromotive force. The magnetic component
of the force orients and axially compresses the polarities of the atoms
in the
electric component of the force. Each component has its own centripetal
force and their orthogonal circuits border a closed space, in which the
substance is polarized, accelerated and compressed centripetal, forming
the
gaseous sphere of the sun. The compressed substance intensifies its oscillations
and emits optical radiation. The centripetal electromagnetic force, crossing
the substance at the speed of light, polarizes it and forms a radial electric
potential. The radial electric potential being perpendicular to the magnetic
field,
generates an angular electromagnetic force and rotates the polarized substance.
Angular electromagnetic acceleration produces the well-known centrifugal
force.
<Electromagnetic angular acceleration is involuntar demonstrated on
You Tube,
the gaseous substance being mercury, rotated to achieve antigravity.>
Differential rotation of the solar sphere.
The exponential increase of electromagnetic pressure towards the center
of
the sun, determines the reverse conversion of energy, from the form of
matter
into the density of electromagnetic circuits. Thus, substance density,
electromagnetic oscillations and temperature, all tend to absolute zero.
The gaseous substance takes the form of a tall dome around the electric
core.
The layer in the dome section is thicker at the equator and thinner towards
the
polar latitudes. The configuration of the dome section is mainly generated
by
the repulsive forces between the polarities of the open circuits of the
magnetic poles, which give the solar system its lenticular shape.
The space between the dome and the electric core is closed by the huge
density and pressure of the orthogonal electromagnetic circuits.
(in the universe, the nuclei of some galaxies are detached or devoid of
substance, the so-called black holes). As a result of the variable size
of the
dome section, the speed of acceleration generated by the angular electromagnetic
force is in relation to the size of the section. Therefore, the differential
rotation
is generated by vectorial composing of the centripetal and angular
electromagnetic forces. The phenomenon turns out to be universal,
also .generated at the level of stellar and galactic systems. Where there
is
substance, objects, there are also forces. The two forces influence each
other,
towards a dynamic balance. In the solar system, it produces the movement
of the planets on orbits, the movement of the Saturnian rings, the successive
detaching of the planets reproduced by the sun, the image of comet tails,
etc