What is electricity?
It is the density gradient of the vector space oriented in closed circuits.
This gradient is the fundamental form of nature's existence, it is the
content
of phenomena in the interpretations of the materialist conception:
matter, magnetism, electricity, gravity.
Matter.
Hydrogen is the solid density of vector space oriented in orthogonally
closed
symmetrical circuits, called the nucleus, "matter". The polarities
of the nucleus,
united in pairs, form a density gradient around the nucleus, with the
role of
internuclear bonds, which compose the elements of the periodic table.
The star is the density of the vector space oriented in orthogonally
closed
asymmetric circuits. Asymmetric, because one of the circuits is completely
surrounded by the other. The completely surrounded vector circuit is called
an electric circuit, the surrounding vector circuit is called a magnetic
circuit.
The electric circuit, also called the core, surrounds and compresses only
a
segment of the magnetic circuit, forming the magnetic axis.
In the uncompressed magnetic circuit, the repulsive forces form by
extension, the gradient of the oriented vector space, called "magnetic
field".
The density of the oriented vector space (of the magnetic field) decreases
radially and increases exponentially towards the surrounded (electric)
vector
circuit. The variation of the density of the oriented vector space, passes
through a density with the best conditions for the composition of the
micro-
vector structures, hydrogen, forming a concentric layer of gas.
The increasing density towards the center, produces decomposition
reactions of the hydrogen structures and a huge spectrum of radiation
- the photosphere. The photosphere with its composition and decomposition
reactions covers a dark sphere with a radius of thousands of km, in which
there is only the density of the oriented vector space, on which the activity
of the photosphere floats. It floats because the high orientation density
of the vector space inside pushes the
hydrogen structures radially,
as Archimedes said. In the activity of the photosphere, a vortex reproduces
orthogonally closed vector space circuits, a new macroscopic vector
structure. The new structure called the sun, having like the mother star
the
photosphere, which covers a dark sphere and the nucleus. The great density
of orientation of the vector space oriented between them, repelled and
launched the sun into orbit. Thus, the sun reproduced by one of the stars
of
the Milky Way galaxy, reproduced in turn the planets, forming the solar
system.
Magnetism.
In macroscopic vector structures, the density gradient of the oriented
vector
space, which completely surrounds the closed orthogonal circuit,
was called the magnetic field, before its nature was known.
Electricity.
Electrical energy is a vector space structure oriented in orthogonally
closed circuits, such as the structure of hydrogen, stars and planets.
Hydrogen vector structures close their vector connection circuits among
themselves and combine, depending on their number, the elements of the
periodic table. Alessandro Volta joined the element zinc to the element
copper, forming a vector dipole - a galvanic element. The galvanic element
is nothing more than an oriented vector space, with open vector polarities
with minus for zinc and plus for copper. These inserted galvanic elements
represent the voltaic pile, a structure of oriented vector space with
its
distinct polarities, minus and plus. The polarities of this pile are
"electrostatic polarizations", which orient the surrounding
space, like the
poles of a magnet. When the poles of the cell are brought into contact
by a
wire, a consumer, simultaneously, the wire is surrounded by the vector
space oriented in orthogonal closed circuits, as Oersted found and is
called a
magnetic field. The magnetic field around the conductor is the gradient
of
the density of the oriented vector space, with the maximum density in
the
conductor, called intensity. The intensity in the wire, in the core of
the earth
and the sun is the maximum density in their electrical circuits, called
the core.
The difference is the vector space oriented through the structure of the
elements in the wire, just as in the photosphere of the sun, the density
of the
vector space is oriented through the hydrogen gas. The increase in the
density of the vector space oriented theough the wire, the intensity,
produces reactions that break down the bonds in the wire structure,
melting the wire. These are the same reactions that break down the
hydrogen structures in the sun's photosphere. In conclusion, electrical
circuits are densities of vector space oriented in orthogonally closed
circuits, in which the increase in orientation density tends to decompose
the
structures of the elements from which the wires are built, into oscillations.
Gravity.
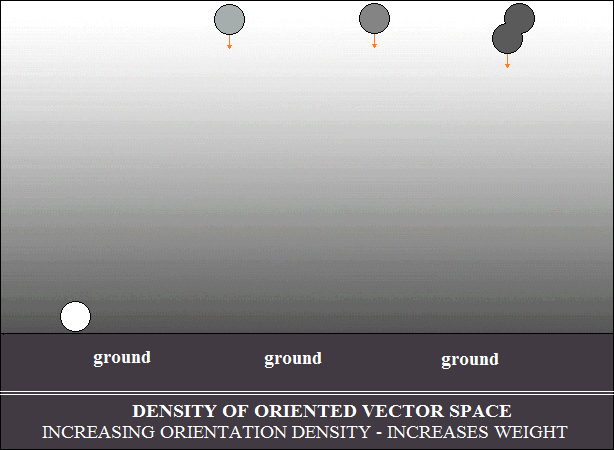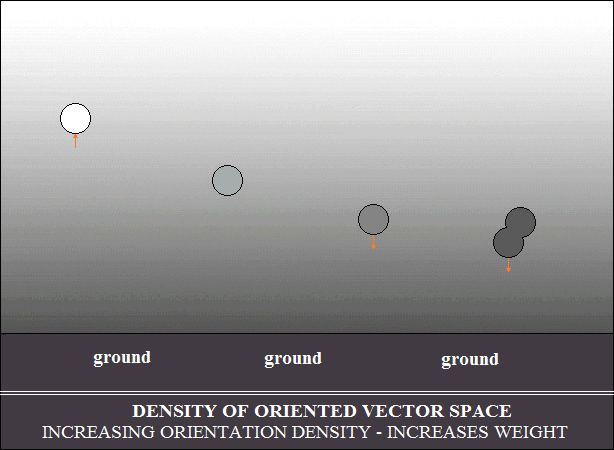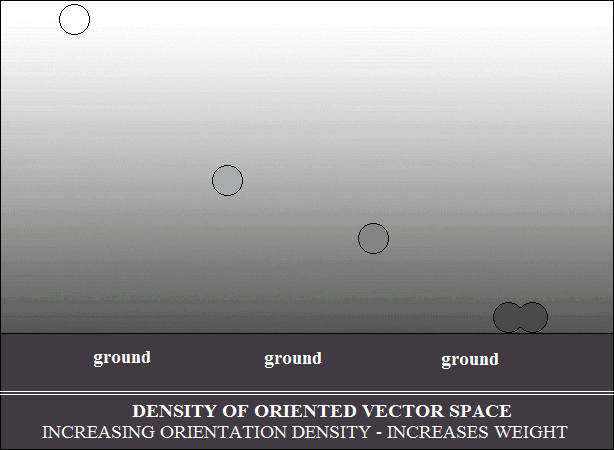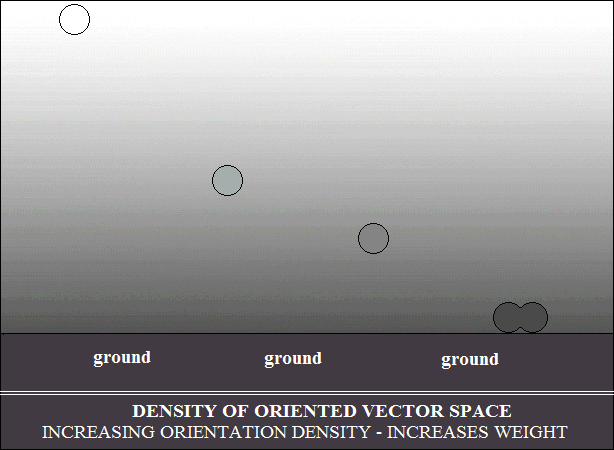
The density gradient of vector space oriented in the earth's atmosphere
selects the movement of bodies, depending on their vector density.
Bodies with low density are pushed radially and stop at equilibrium with
the
density gradient, as shown in the drawing below. In other words, heavier
bodies, in falling, stop at the equilibrium with the density in the gradient.
These interactions justify Aristotle's thinking and the laws of Achimedes
and exclude the existence of Newton's and Einstein's gravity. Very
interesting are the tangential movements at gradient, the flight of the
airplane.
Until now, the flight of the airplane was attributed to the lifting force
of the air.
In reality, the speed of the movement orients the vector space around
the
airplane in the direction of the movement. The repulsive forces in the
space
oriented in the same direction decrease the density of the oriented vector
space around the plane. During flight, the plane is accompanied by a space
with low density in relation to the gradient density, which balances the
density of the plane, the weight. The flight of Halley's comet, the orientation
of its tail as it circles the sun, shows, as beautifully as could be,
the
interaction of the density of the sun's oriented vector space, with the
density
of the space oriented by the comet's speed such as the hypostases of "lift"
and "gravitational assistance". In nature, the densities of
oriented vector
space can also be amplified. During the Earth's rotation, the gradient
on the side of the hemisphere facing the sun is amplified by the solar
gradient and raises the level of the oceans - the tides.