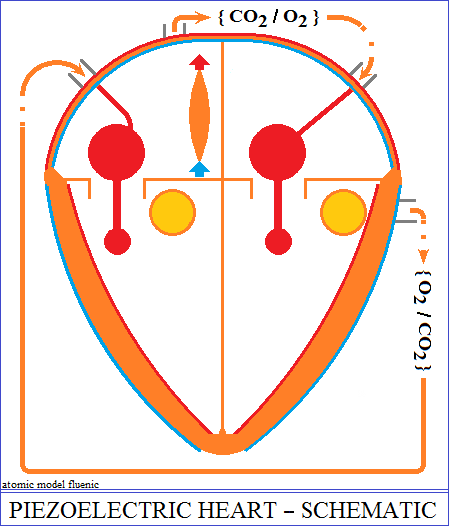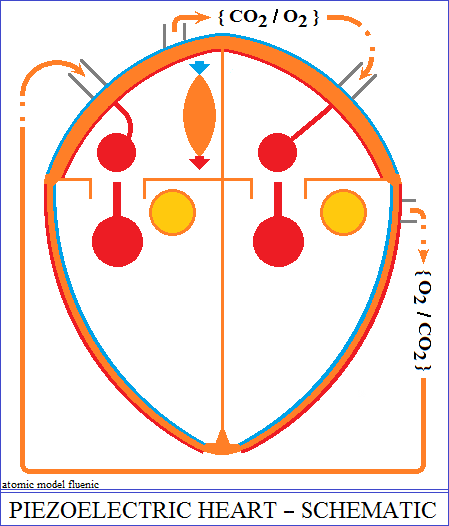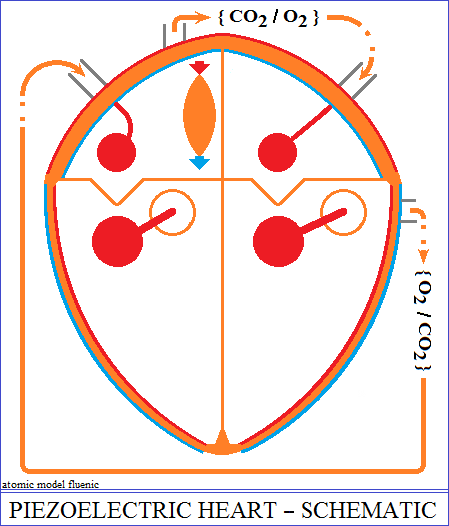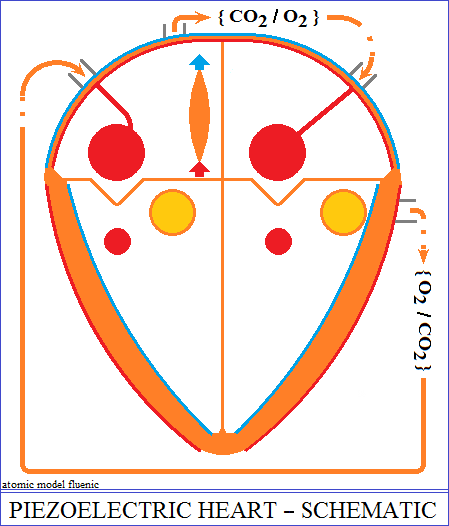
The structure of the heart
The heart is the mutual interaction between two piezoelectric oscillators.
It is a muscle
composed of two pumps, right and left, separated by a support structure called
the septum.
The pump on the right and the pump on the left of the septum each have two
chambers, an
atrium and a ventricle, with variable volumes. The pump on the left pushes
the oxygenated blood
for metabolism. The pump on the right pushes the blood resulted from the metabolism
to the
lungs for reoxygenation and the circuit closes. Only the right atrium has
a cellular structure called
a node. The node transforms the variation of the pressure in the right atrium
into electrical
polarities applied to the pumps, in order to contract and dilate alternately
the atrial and the
ventricular volume. The ventricle has two valves that ensure the admission
and evacuation of
blood. So, while the contraction of the ventricle evacuates the blood, the
dilation of the atrium
accumulates a new volume of blood for a new filling of the ventricle.
The piezoelectric phenomenon
Alesandro Volta, repeating Galvani's experiments, found that the electricity
that appears when
the muscle is in contact with two different metals is not of the organic tissue,
but of the contact
between the metals. Volta thus interpreted organic tissue as the means of
contact between the
two different metals, which he replaced for demonstration, with another means,
inventing the
electric cell. Volta thus ignored the effect of the movement of organic tissue.
The appearance of
the electric cell started the invention of the electron, to explain the electrical
phenomenon and
implicitly the current of electric charges (there were no alternatives). Now
I can say that Luigi
Galvani demonstrated through his experiments, the piezoelectric effect, before
it was discovered.
Galvani's demonstration was possible because the piezoelectric phenomenon
is the essence of
the notion of animal, of movement, of compression and dilation, etc.
Piezoelectric oscillator
The piezoelectric properties consist in the action of compressing and expanding
the size of a
structure in one direction. Compressing the dimension in one direction, refulates
on the
perpendicular direction, in order to preserve the volume. The modification
of the structures
forces the elasticity of the vector circuits of connection between the atoms
or molecules of the
structure, which on the refulated surface break due to lack of continuity
and form open polarities
of a certain sign. The other refulated surface has open polarities with the
opposite sign.
It follows that the structure must have a vector-ordered geometry, because
contraction and
expansion reverse the signs of polarities. At the end of the action, the size
changes return to
normal, but the elasticity of the bonding circuits continues to oscillate,
damped or maintained,
with the alternating reversal of the polarities, synchronous with the expansion
/ compression
- this is the piezoelectric oscillator.
Mineral and organic piezoelectric structures:
Mineral structures are atomic structures, with the frequencies of large oscillations
and variations
of small dimensions. Organic structures are molecular structures, with small
oscillation frequencies
and larger variations in size. From this point of view, the heart is an association
of piezoelectric
structures. The atrial node transmits its electrical polarities directly to
the atrial and inverted
muscles, to those in the ventricles.
Function creates the organ
The organs of the animal body are created of their functions, through natural
selection: claws,
hair, feathers, bone, heart, etc. are evolutions of their functions. Thus,
the heart, the heart
muscle and the sinus node are electrically insulating molecular structures
and have the
piezoelectric properties, characteristic of the quartz crystal, created by
their functions.
Nerve
Energy with vector properties, have organized microscopic material structures
consisting of
closed vector circuits - hydrogen atoms. In turn, hydrogen atoms bind to each
other through the
same closed vector circuits and form the atoms of the elements. Macroscopically,
cosmic
bodies interact with each other from a distance, through energy flows with
vector properties, in
the form of closed vector circuits (magnetism) and open (polarities). The
piezoelectric functioning
of the heart shows that nature, the energy with vector properties, has created
an organ with the
function of an insulating guide, through which the energy with vector properties
in open circuit is
transmitted at a distance - nerve. Energy with open-circuit vector properties
cannot be seen
under a microscope, it being the same energetic nature as the electrostatic
field.
Instead, the guide of energy, the "nerve", having as structure the
same energy with vector
properties, but in closed circuits (electrical and magnetic), with material
shapes and dimensions,
can be studied under a microscope. The nerve can be compared to an isolated
electrical
conductor, in which the conductor is missing, being replaced by energy with
open-circuit vector
properties. Through these "wires", the node transmits vector polarities
directly to the atria and
inverted to the ventricles. Reversed transmission of polarities achieves the
pump function,
optimized by the septum and the tendon cords of the valves. Practically by
inversion, the atria
accumulate the amount of blood necessary to refill the ventricles, while the
ventricles evacuate
the blood, cushioning the exaggerated variation of the pressures in the blood
circuit.
The rhythm of the heartbeat
The atrial node oscillates at a normal equilibrium, in relation to the size
of the animal organism,
being actioned by the variation of the atrial pressure. At large pressure
variations, the oscillations
of the node increase in amplitude and the frequency decreases. At small pressure
variations, the
oscillations of the node decrease in amplitude and the frequency increases.
Metabolism, cellular
chemical reactions, consume energy (oxygenated blood) depending on effort.
Increased energy consumption levels the pressure variation in the right atrium
and the atrial node
increases the frequency of oscillations, ensuring the blood flow required
for metabolism.
Rest reduces energy consumption, increases the variation of pressure in the
right atrium and
the atrial node reduces the frequency of oscillations, decreasing blood flow.
Play muscles how the node sing and the node sing how the muscles play.