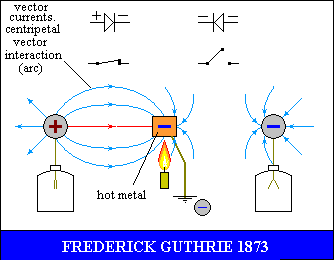
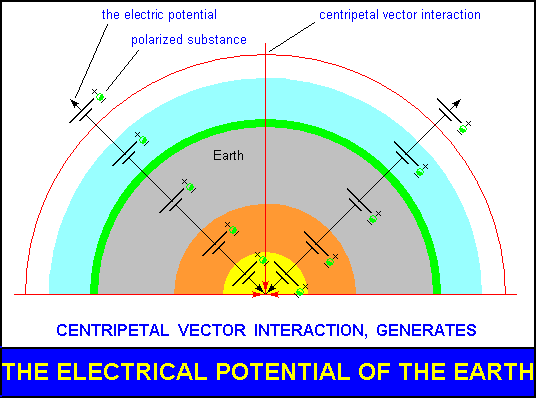
making a double tor oscillator
- atom of hydrogen or nucleon.
Hydrogen has stability, orthogonal symmetry and is the first element of
the table.
The two vectorial currents are the known electric and magnetic fields.
Vectorial current connects nucleons amongst them,
adding step by step new elements in the table.
The symmetry and stability of the first element
is changed by each and every added nucleon, up to the time elements become
unstable, radioactive.
Such modifications determine the properties of elements.
Vectorial current
Vectorial current is the closure of the two orthogonal orientations
(electric and magnetic)
The property of semiconductor to set or not vectorial current by PN junction,
comes from the symmetry of vectorial currents.
Some atoms are missing orthogonal symmetry of vectorial currents.
Therefore, their polarity is not induced to neighboring atoms, in order
to make vectorial current.
The abundance of radiations also contribute to the lack of symmetry (photons,
temperature)
At the opposite "pole", electric and magnetic superconductivity
is found.
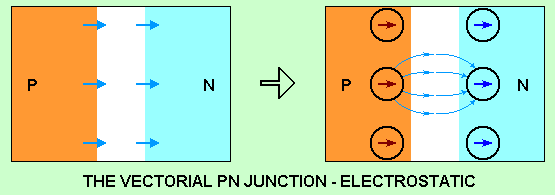
Vectorial junction PN
Electrostatic:
The junction of P and N structures make a capacity, with the two electrostatically
loaded structures.
The polarities of junction, the field lines, are electrostatically unified.
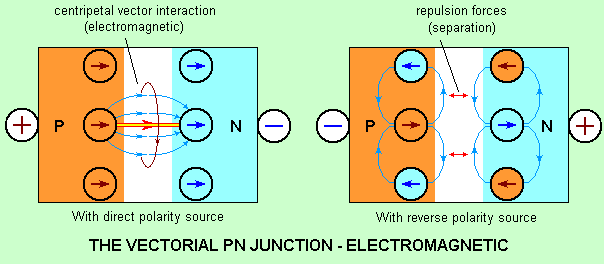
Electromagnetically:
Direct supply, closes vectorial currents by all the polarities
of the junction and
launches centripetal interaction, by setting a current bridge- (electric
arc)
Obviously, the arc can be performed with pure metal junctions as well,
supplied in DC and AC
Inverse supply, commutes polarities which are not inversed on the
new polarities, opposed now, and
generates eddy currents, which interrupt vectorial current amongst structures
(the bridge is down).